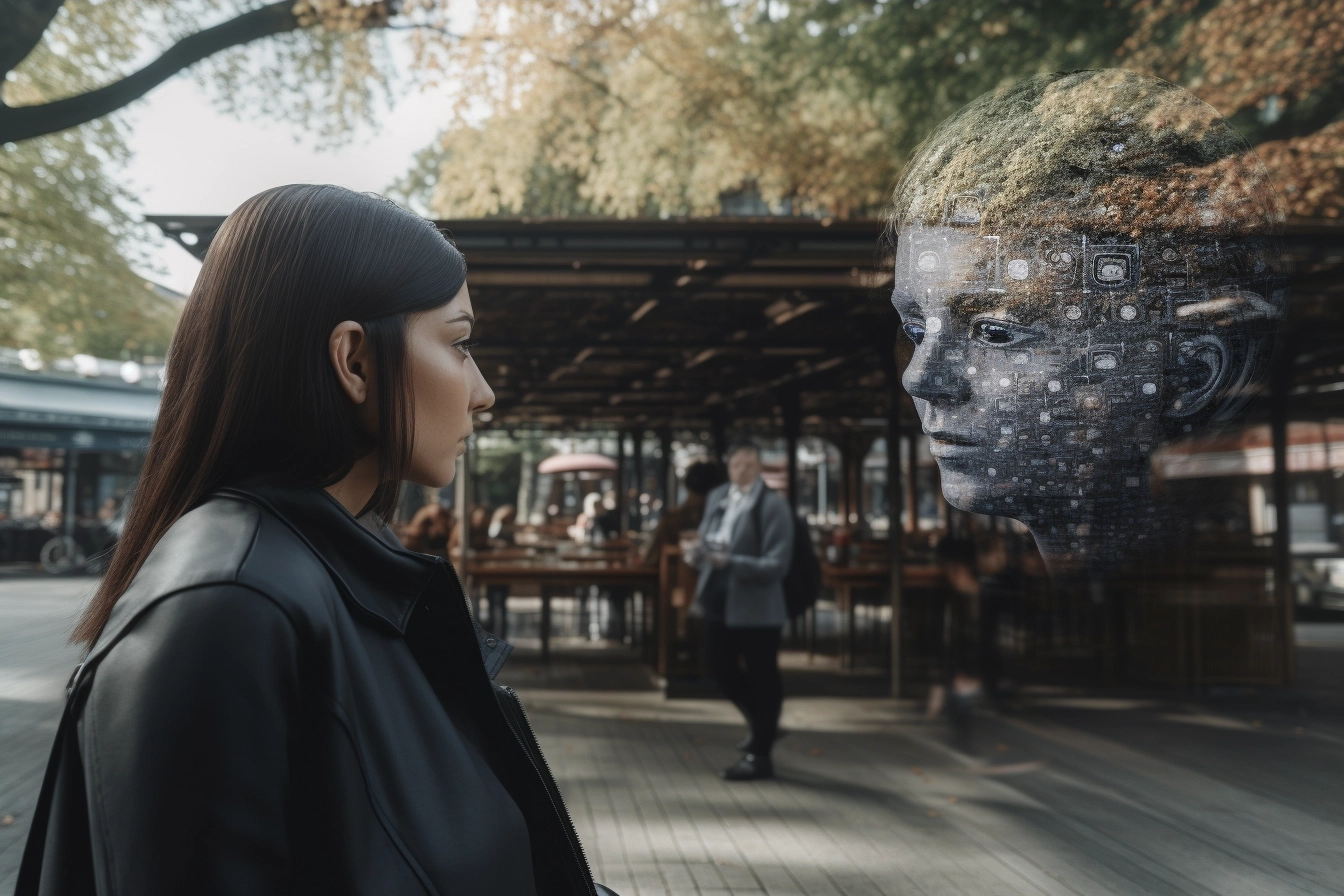
In recent years, our team at Google has been making significant strides in the development of quantum computing, a revolutionary technology that has the potential to solve complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. One of the major challenges we’ve faced is reducing errors in quantum computations, which can cause incorrect results and hinder the development of practical applications.
Reducing Errors through Qubit Consolidation
Our researchers have been working on a novel approach to reduce errors by increasing the number of qubits used in a single computation. In traditional quantum computing, each physical qubit is treated as an individual unit of information that can take on richer states than classical bits (0 and 1). However, when we increase the number of qubits used in a computation, the likelihood of errors increases exponentially.
The Breakthrough: Treating Qubits as Logical Units
Our team has experimentally demonstrated that it’s possible to reduce errors by treating multiple physical qubits as one logical unit. This approach allows us to operate quantum computers more efficiently and increase the accuracy of computations.
To achieve this, we divided a group of 49 physical qubits into smaller clusters, each containing several qubits. By pooling these qubits together, we were able to create a single logical qubit that could perform calculations without errors. This breakthrough represents a significant shift in how we operate quantum computers and has the potential to greatly improve their accuracy.
Comparing the Performance of Logical Qubits
To test our new approach, we compared the performance of logical qubits created from 17 physical qubits with those created from 49 physical qubits. The results were striking: the logical qubit made from 49 physical qubits outperformed the one made from 17 qubits in several key areas.
This breakthrough is a significant step forward for quantum computing and has the potential to unlock new applications in fields such as medicine, finance, and climate modeling. However, there’s still much work to be done to perfect this technology and ensure its safe and reliable operation.
Quantum AI: The Future of Computing
Our progress toward quantum error correction is just one example of the exciting developments happening at Google in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). Our researchers are working on a range of projects that combine AI with other cutting-edge technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing.
Introducing PaLM API & MakerSuite
We’re proud to announce the launch of PaLM API and MakerSuite, two new tools designed to make it easier for developers and businesses to explore and prototype with generative AI applications. With PaLM API, users can try out new APIs and products that provide a safe and scalable way to start building with Google’s best AI models.
MakerSuite is a prototyping environment that allows users to quickly test and refine their ideas using Google’s latest AI technologies. This platform is perfect for developers who want to explore the possibilities of generative AI without worrying about setup or infrastructure costs.
What Can You Do with PaLM API & MakerSuite?
With PaLM API, you can:
- Try new APIs and products that make it easy, safe, and scalable to start building with Google’s best AI models
- Experiment with cutting-edge technologies such as natural language processing and machine learning
- Quickly test and refine your ideas using a range of tools and templates
MakerSuite offers a range of features and tools designed to help you prototype and develop generative AI applications. With MakerSuite, you can:
- Use a range of pre-built templates and workflows to get started quickly
- Experiment with different models and parameters to optimize performance
- Collaborate with others in real-time using built-in commenting and feedback tools
Unlocking Human Potential with Generative AI
Our goal is to help people unlock their human potential by providing access to cutting-edge AI technologies. With PaLM API and MakerSuite, we’re making it easier for developers and businesses to explore the possibilities of generative AI.
However, as with any emerging technology, there are risks and limitations associated with its use. That’s why we’re committed to engaging with industry experts, educators, policymakers, civil rights, and human rights leaders to learn about the many possible applications and limitations of this technology.
Meet Bard: Your Creative Collaborator
We’re also excited to introduce you to Bard, a new interface designed to enable users to collaborate with generative AI. With Bard, you can:
- Get creative assistance from an LLM that provides insights and ideas on demand
- Use natural language processing to interact with the system and refine your work
- Collaborate with others in real-time using built-in commenting and feedback tools
Our team is committed to developing new applications for generative AI that help people unlock their human potential. We believe that by providing access to cutting-edge technologies, we can empower individuals and organizations to achieve great things.
Conclusion
We’re proud of the progress our researchers have made in quantum error correction and excited about the possibilities offered by PaLM API, MakerSuite, and Bard. These innovations demonstrate Google’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with AI and related technologies.
As we continue to develop new applications for generative AI, we’ll be working closely with industry experts, educators, policymakers, civil rights, and human rights leaders to ensure that these technologies are used safely and responsibly.
Learn More
To learn more about our research in quantum error correction, PaLM API, MakerSuite, Bard, or other cutting-edge AI technologies, please visit the following resources:
We’re excited to share our progress with you and look forward to continuing the conversation about the possibilities of generative AI.